Recently, Kou Menggang, a PhD student from the Department of Engineering Science, Faculty of Innovation Engineering at Macau University of Science and Technology (MUST), published his latest research results in the international authoritative journals Information Fusion and Advanced Engineering Informatics. The studies proposed innovative solutions leveraging large model knowledge distillation technology for solar and wind energy forecasting problems respectively, providing strong support for promoting the efficient grid integration of renewable energy and the safe operation of smart grids.
The latest research on solar energy forecasting was published in Information Fusion (Impact Factor: 15.5, top 1.7% in JCR Computer Science, CAAI Class A recommended journal), a top international journal in the field of AI and information fusion. The paper is titled “PMFM-kdTransformer: An enhanced multi-modal fusion architecture leveraging knowledge distillation for intra-hour solar irradiance prediction.” The paper proposes an enhanced multi-modal fusion architecture, PMFM-kdTransformer, which processes cloud images, meteorological data, and irradiance sequences in parallel. Combined with knowledge distillation technology, it significantly reduces computational costs while improving prediction accuracy. This method achieved an average improvement of 7.92% across seven evaluation metrics and is particularly suitable for scenarios lacking expensive total-sky imagers, offering a practical solution for real-time power forecasting in photovoltaic power stations.
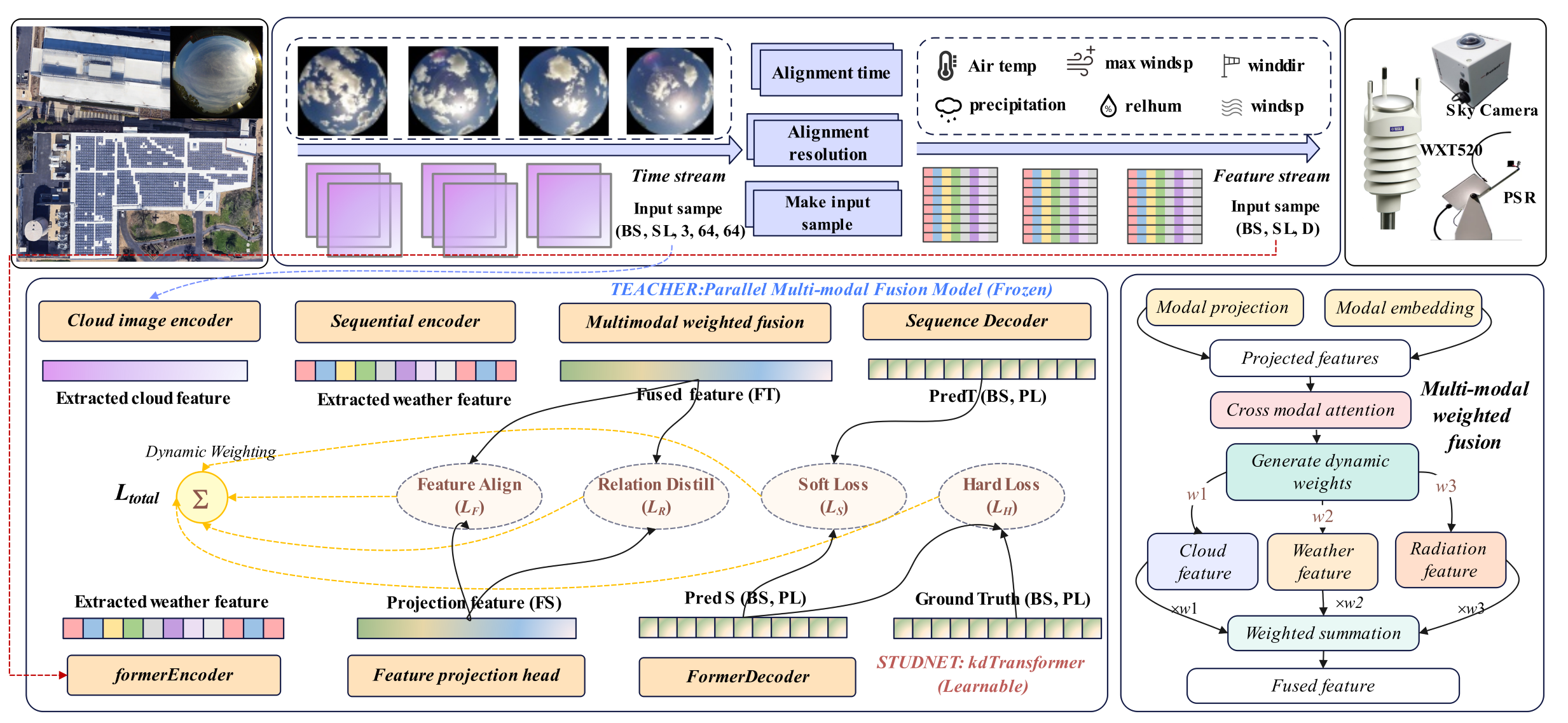
∆ Research one: diagram of the proposed solution
The wind energy research, titled “Ultra-short-term wind power forecasting jointly driven by anomaly clustering and graph convolutional recurrent neural networks.” was published in Advanced Engineering Informatics (Impact Factor: 9.9, top 2% in JCR Engineering, CCF Class B recommended journal). This research was recently selected as an ESI Global Top 1% Highly Cited Paper, marking its widespread influence and peer recognition in the international academic community. Addressing ultra-short-term regional power forecasting for large-scale wind farms, the study innovatively combines anomaly detection, cluster analysis, and graph convolutional neural networks. It achieved a prediction accuracy improvement of over 50% while shortening training time by 70.84% and reducing GPU memory usage by 94.04%, providing efficient technical support for the real-time scheduling of regional wind power clusters.
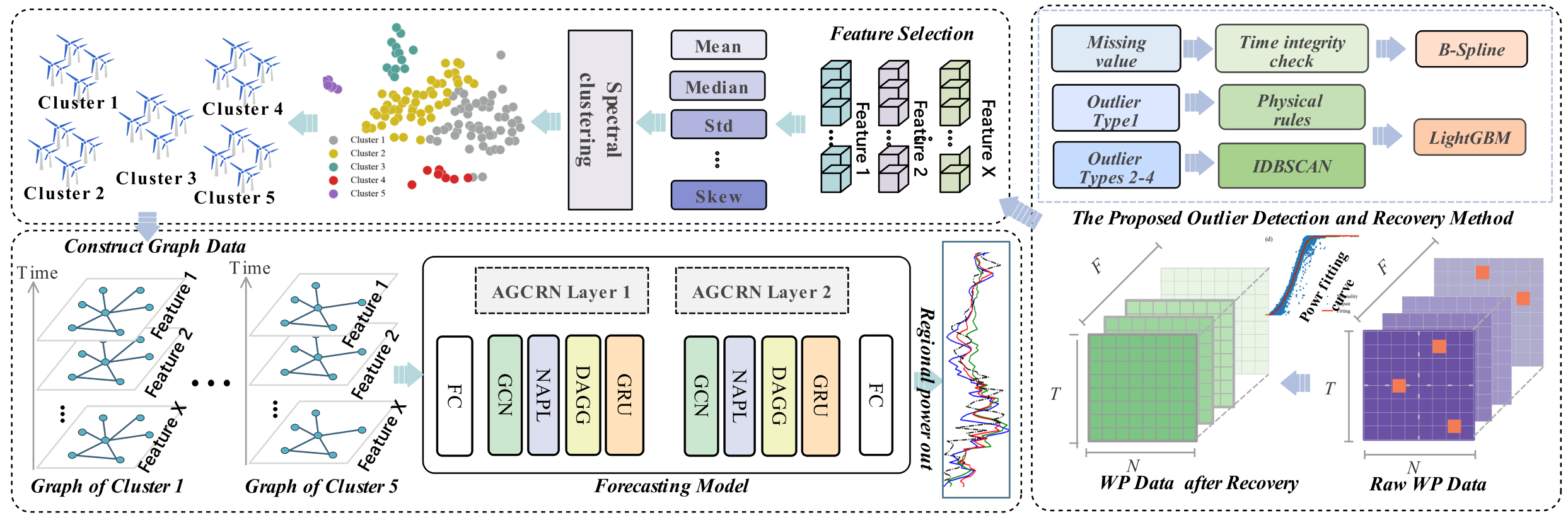
∆ Research two: diagram of the proposed solution
Both studies designate the Macau University of Science and Technology as the primary affiliation. They were completed by PhD student Kou Menggang, serving as the first author and corresponding author respectively, in collaboration with research team members Li Runze and Qian Yuansheng, and were supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macao SAR. These research results reflect MUST's scientific research innovation capabilities in the interdisciplinary field of artificial intelligence and energy engineering, providing important technical references for the large-scale accommodation of renewable energy and the stable operation of power grids.
Paper links:
1. Information Fusion: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2025.104043
2. Advanced Engineering Informatics: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2025.103137

∆ Kou Menggang





